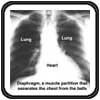
Your on-line source for reliable and unbiased information about the evaluation & treatment of heart disease.
Welcome to Heartsite.com
This web site was designed to provide information to patients who are being evaluated and treated for a heart-related complaint. All contents are reviewed by physicians to ensure accuracy. Our objective is to educate. The information on this web site is meant to supplement and NOT to replace those obtained from your personal physician. Please consult your physician because a specific disease, test or treatment may not be applicable to your case. To facilitate understanding, tools and lectures were designed from the ground up instead of scanning in traditional textbooks or videotaping a slide presentation and then modifying it for use on the Internet. This site includes panoramic views, 3D animation, online lectures, narrations, streaming instructional video, and easy to understand animated examples.
All of the material on this web site is made up of original work designed by the web site team and reviewed by the Medical Editor (see below).

Other topics are in the works. Please visit us again!
Acknowledgement
The Educational content material was designed and developed by Abdulla M. Abdulla, M.D., F.A.C.P., F.A.C.C. He is a Clinical Professor of Medicine and a prior Chief of Cardiology at the Medical College of Georgia. He is Board Certified in Internal Medicine, Cardiology and Interventional Cardiology and has published multiple scientific articles in text books and major medical journals. He is also the recipient of a dozen Teacher of the Year awards from the Medical College of Georgia, is a former Teaching Scholar of The American Heart Association and is nationally recognized as an expert on Internet-based Medical Education.
We pledge to make every effort to add new topics or updates on a timely basis. Please visit again!
This Site was Last reviewed on January 15, 2022
 This site complies with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information:
This site complies with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information:
verify here.
©1999-2017, 20XXA.S.M. Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved, including design and all graphic contents & animations